AI Tool Can Scan a Retina, Predict Heart Disease Risk in Under a Minute
Doctors have long been able to assess a person’s risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and other diseases by manually looking at the retina.
QUARTZ can reportedly fill this gap. A team of researchers from Cambridge University, St George’s University of London, and University College London created the tool by obtaining images of 95,463 participants’ retinas, which came from UK Biobank (a voluntary biomedical database) and the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC). They used these images to train a machine learning algorithm to analyze the width and tortuosity of the retinas’ blood vessels. Then the team combined these analyses with the participants’ known cardiac outcomes to create a heart risk prediction model.
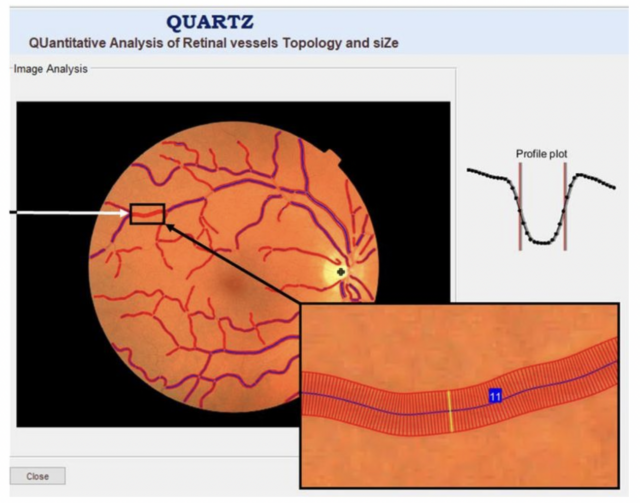
(Image: Rudnicka et al/British Journal of Ophthalmology)
Now the researchers can scan anyone’s eye and obtain key cardiac insights in a matter of seconds. In their published last week in the British Journal of Ophthalmology, the researchers write that a person’s retinal vasculature snapshot, combined with risk factors like smoking, previous heart attacks, and drugs to treat high blood pressure, can be used to predict that person’s risk of cardiovascular disease at the same accuracy rate as current, less convenient methods.
As we last week in our report on the White House’s proposed “AI Bill of Rights,” machine learning algorithms are as biased as the data they’re based on, and QUARTZ is no exception. The Verge that UK Biobank’s data happens to be 94.6 percent white, meaning there’s little room to determine whether QUARTZ predicts heart disease risk as accurately among people of color. The researchers also note in their study that UK Biobank and EPIC data are from a healthier population than is representative of the UK (and the world) at large.
But it’ll be a while before QUARTZ finds its way into real-life medical settings. As with any other novel medical tool or system, QUARTZ requires rigorous testing before it can become eligible for use on regular patients. The team hopes to confirm the tool’s efficacy with a wider, more diverse population during this time.
Now Read: